Ethereum's Layer 2 Scaling Solutions

If you've ever tried sifting through the technical mumbo jumbo of Layer 2 scaling solutions like Rollups and Sidechains, you know how much of a rollercoaster it can be. Trust me, it's not you; it's the space. But I'll break it down for you:
You have rollups acting as express lanes for transactions, with Optimistic ones being the go-to for general purposes and Zero-Knowledge ones prioritizing privacy. Validiums are cost-cutters for the NFT market, and sidechains are the side streets for less hefty transactions.
Key factors in choosing a Layer 2 include EVM compatibility and efficient data handling. And while you're still getting your head around these, the tech space is buzzing with breakthroughs like Recursive ZK Snarks and STARKs that promise to push the boundaries even further.
The Ethereum Layer 2 scene is booming, with various types of technologies like Arbitrum, Optimism, Scroll, Kakarot, and Taiko making big security progress. There's a lot of mixing going on: some projects once independent are now considering joining Ethereum's Layer 2 club, while others are adapting to become validiums, a sort of halfway house between a fully decentralized and a centralized system.
As this mix-up continues, we're seeing a trend where projects are becoming more diverse. Some want to stay close to Ethereum, but can't go all in just yet. Others need to offer their users stronger security without going full blockchain. Non-financial apps like games or social media are also dipping their toes in, needing a balance between security and cost.
The big question is, with all these options, what's the best fit for developers' app? It depends on how much you value security versus scalability. Rollups are secure but come at a higher cost, while validiums can be cheaper but with a risk of data loss. And if you just want something really cheap, you can go for a disconnected system, though it's less secure.
The future of Ethereum includes upgrades like EIP-4844, which will make data cheaper and more abundant, affecting these choices. Applications will have to weigh up the cost of security against their specific needs.
Reading Ethereum is another crucial aspect. It's all about how well these Layer 2 systems can understand and react to Ethereum's own changes. If Ethereum has a hiccup or an upgrade, the Layer 2s need to be able to respond accordingly to maintain their connection and security.
So, Layer 2's connectedness to Ethereum boils down to two things: how well they can withdraw back to Ethereum and how accurately they can read Ethereum's blockchain. Different projects will prioritize these differently, and as technology improves, we might see more shift towards tighter integration with Ethereum.
The Layer 2 Landscape
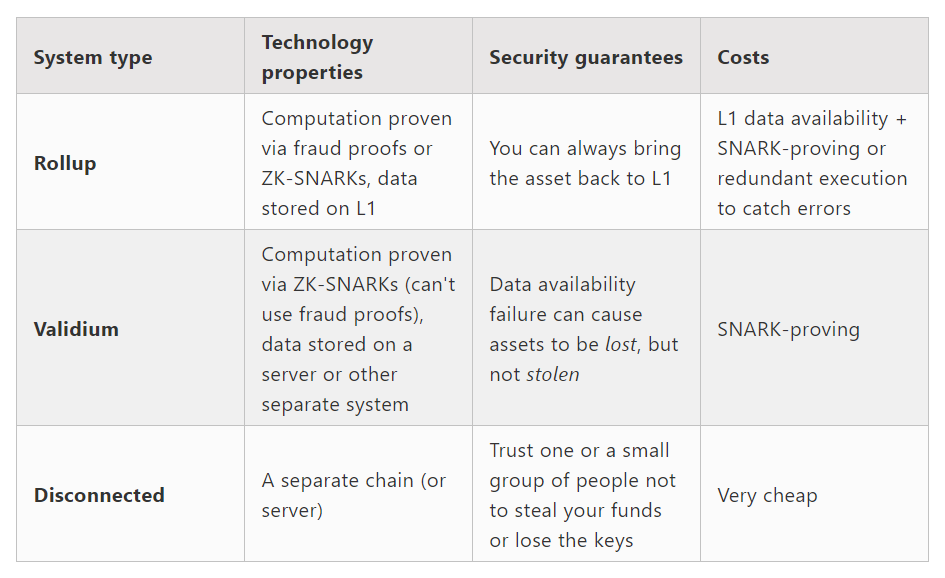
Broadly speaking, layer 2 solutions fall into three main buckets: rollups, validiums, and sidechains. However, there is also much nuance within each category:
Rollups batch transactions off-chain while generating proofs that allow results to be posted back to Ethereum. They come in two flavors:
Optimistic Rollups (ORs)
They assume transactions are valid by default, but have a fraud-proof mechanism for challenges. Lower costs than ZK rollups, but lack the privacy feature.
Examples include Arbitrum, Optimism, Metis, Mantle, Base, and Fuel.
Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZKRs)
They use validity proofs (aka Zero Knowledge Proof or ZKP) to cryptographically prove correctness. More complex to implement than ORs, but offer privacy.
Examples are Starknet, zkSync, Aztec, Polygon Hermez, Loopring, Scroll, Linea, and Taiko.
Validiums
Like ZKRs, validiums also generate proofs for off-chain computation but keep data availability off-chain. Cheaper than rollups, but have liveness risks if data is unavailable. Examples include Immutable X, Sorare, and zkPorter.
To visualize the security/cost tradeoffs:
When to Use Each Approach
- ZK Rollups make sense for privacy-sensitive apps like confidential transactions.
- Optimistic Rollups strike a good balance for mainstream contracts like swaps.
- Validiums can reduce fees for NFT platforms while limiting liveness risks.
- Sidechains are suitable for low-value transaction volume, like gaming dapps.
For many projects, a gradual shift from sidechains to validiums to eventual rollup integration may be prudent based on priorities around security, fees, and seamless L1 interoperability.
Key Differentiating Factors
Beyond the high-level categorization, here are some other key variables to consider:
EVM Compatibility - Systems like zkSync support solidity/EVM to ease migration. Non-EVM chains have a higher barrier to porting.
Statefulness - Stateful systems currently used by the vast majority of blockchains enable more complex apps but require fraud proofs or checkpoints. Stateless systems like StarkNet however rely solely on validity proofs.
Modular Verification - Allowing portions of blocks to be verified incrementally improves costs without sacrificing security.
Data Availability - Storing data on-chain maximizes robustness but increases costs. Off-chain storage needs well-incentivized redundancy.
Bridging - Cross-rollup bridges are important for asset composability across ecosystems.
Ongoing Innovations
The layer 2 landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with noteworthy innovations across several fronts:
Recursive ZK Snarks - Allow provably correct chains of ZK proofs, reducing proof sizes. Used by Polygon Hermez, zkSync 2.0.
STARKs - Alternative to SNARKs with transparent setup, but currently have large proof sizes.
Hybrid Models - Combining validity proofs for computations with other proof mechanisms.
Data Sharding - Allows Data Availability Sampling or splitting data across shards to reduce storage costs.
The Road Ahead
Ethereum's base layer continues to scale with upcoming upgrades like proto-danksharding. This will drastically reduce L2 gas costs over time, allowing very high L2 throughput with Ethereum-level security - the best of both worlds.
Deeper L2 interoperability and bridges will also allow assets and contracts to seamlessly flow between ecosystems. End users may not even realize they have switched L2s.
For developers and users navigating the multitude of layer 2 offerings, understanding the core design nuances is essential. Each project makes slightly different tradeoffs that suit particular needs. But broadly speaking, the ecosystem is moving towards rollup-centric architectures that maximize decentralization while offering internet-scale throughput, abundant data availability, and rock-solid security assured by Ethereum at the base layer.

